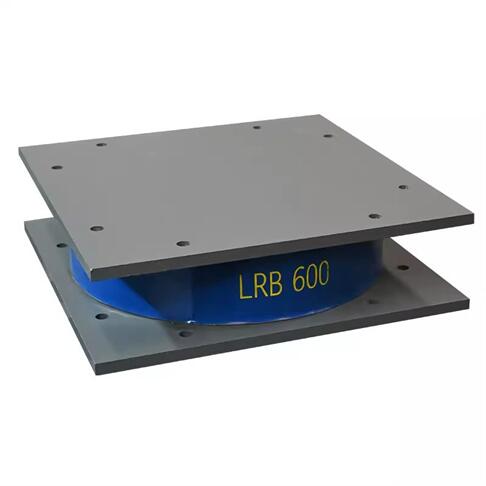
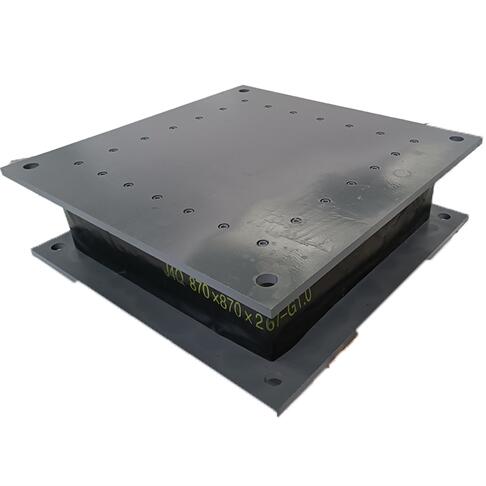
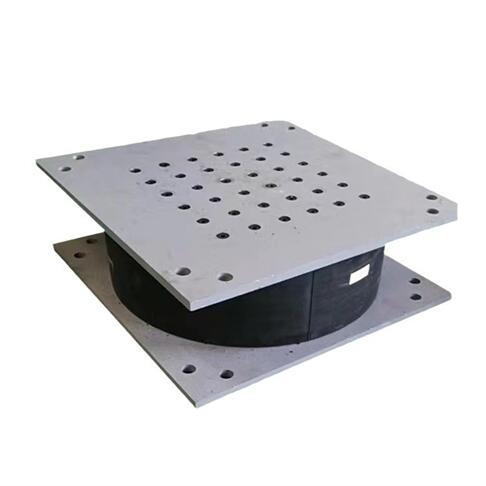
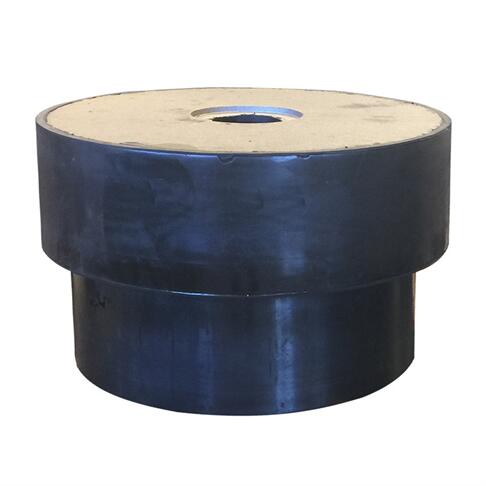
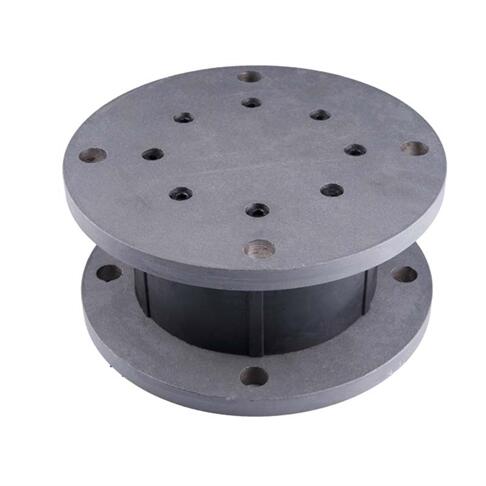
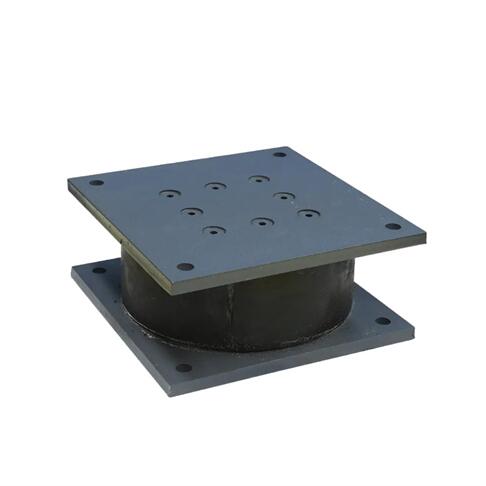
Lead Rubber Bearing(LRB) Specifications
| Material: | NR or CR |
|---|---|
| Shear modulus: | 0.8 MPa, 1.0 MPa, 1.2 MPa |
| Tensile Strength: | 15Mpa MIN |
| Elongation at Break: | 500% MIN |
| Working temperature: | -25 °C to +60 °C |
| Lead core: | Single or multiple |
| Diameter: | φ500,φ600,φ700,φ800,φ900,φ1000 |
| Shape: | Rectangular and round |
What is Lead Rubber Bearing(LRB)
The lead rubber bearing is formed by pressing a lead core into the center of the RB bearing. After the lead core is pressed in, it integrates with the rubber bearing and follows the shear deformation. This bearing is an isolation device with a damping mechanism composed of a stable recovery device of the rubber bearing and an energy absorption device of the lead.
Lead is a metal with good plastic deformation and energy absorption capabilities. Lead rubber bearings are also one of the earliest bearings used in seismic isolation structures. Lead rubber bearings have been widely used in engineering due to their excellent mechanical properties, relatively simple structure and high cost performance.
Types of Lead Rubber Bearing(LRB)
- Lead Bearing Basic Performance
- Basic Mechanical Properties
Basic performance of Lead Rubber Bearing(LRB)
(1)Energy absorption capacity of lead damper:
Rubber itself is a material that is easily deformed by tension and compression. When made into a bearing alone, it will deform greatly after force is applied. Engineering rubber bearings are composed of thin steel plates and thin rubber layers. The steel plates have excellent restraining effect on the vertical deformation of rubber, and the vertical compression stiffness is very high. However, like natural rubber bearings, the tensile stiffness of LRB bearings is low, about 1/7 to 1/10 of the compression stiffness.
(2)Horizontal deformation capacity of LBR bearings
The steel plate constrains the vertical deformation of the rubber but has no effect on its horizontal deformation. At the same time, the lead core can well follow the deformation of the bearing and absorb seismic energy. The horizontal performance of the LRB bearing is stable. Due to the presence of the lead core, the horizontal deformation of the bearing can be limited. The horizontal deformation of the seismic isolation structure equipped with the LRB bearing is smaller than that of the RB bearing (without considering the effect of external damping).
The hysteresis performance of the lead rubber bearing can be represented by a bilinear model. The thin solid line is the hysteresis characteristic of the rubber bearing. The horizontal characteristics of the LRB bearing are the superposition of the horizontal performance of the rubber part and the lead part. The lead rubber bearing can show a stable bilinear hysteresis characteristic when the shear deformation is 250%.
Durability of Lead Rubber Bearing(LRB)
The LRB bearing is basically the same as the RB bearing. Even after 100 years of use, the internal rubber of the seismic isolation rubber is still intact. A survey shows that the characteristics of the LRB bearing remain basically unchanged after 10 years of use, and it is predicted that its performance will only decrease by 3% after 60 years.
Features of Lead Rubber Bearing(LRB)
(1)Suitable horizontal stiffness. Satisfy the earthquake vibration and normal displacement. It can enlarge the vibration cycle to 1.5 to 3 seconds.
(2)Stable vertical stiffness and excellent vertical loading capacity.
(3)Excellent damping performance.
(4)Good energy dissipation capacity.
(5)Adjustable lead core area. It can suit different damping ratio through adjusting wire diameter and sectional area.
(6)Excellent durability, cycle fatigue resistance, acid and alkali resistance.
(7)Long lifespan. 60–80 years long lifespan for durability.
(8)Easy installation and replacement for lower maintenance costs.

Characteristics of lead rubber bearings (LRB)
Lead rubber bearings adjust the damping by the size of the lead core. When the lead core diameter increases, the yield force becomes larger and the damping amount increases, but an overly large center hole will also have a negative impact on the performance of the bearing.
Application of Lead Rubber Bearing(LRB)
Lead Rubber Bearings can be used in the construction of new structures, or to enhance an existing structure’s strength and resistance to seismic forces. Under normal conditions, they function as regular deformation bearings, and are thus particularly suitable for structures with limited space availability, where the installation of separate bearings and seismic protection systems is not possible.

Lead Rubber Bearing Packing
The packaging of lead-core rubber bearings is usually carried out in bags, wooden cases, pallets or according to customer requirements.
Hengshui Lu Chen New Material Technology Co., LTD.
We are a professional manufacturer and exporter that is concerned with the design, development and production of lead bearing.
All of our products comply with international quality standards and are greatly appreciated in a variety of different markets throughout the world
In an earthquake, unisolated buildings will vibrate back and forth in different directions due to inertial forces, resulting in building deformation and damage. The lead rubber bearing can separate the vibration of the top and bottom structure, expand the natural vibration period, and reduce the seismic force. The lead plug will slide together with the laminated rubber during an earthquake, but convert this movement energy into heat, thereby effectively reducing the inertial force of the building, thereby slowing down the vibration of the building. At the same time, the rubber part will maintain its original shape due to high elasticity.
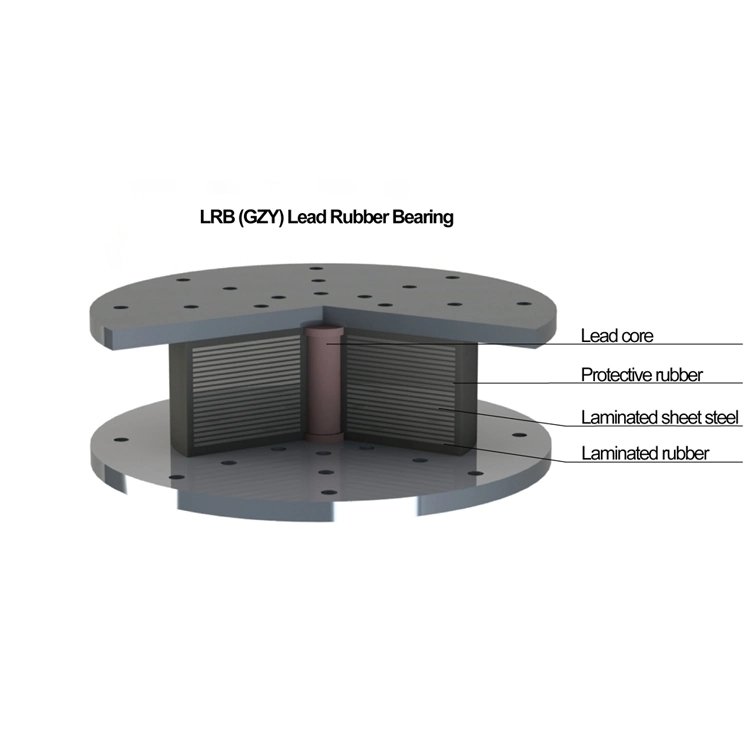
The lead rubber bearing consists of a laminated elastic bearing pad, upper and lower sealing connection plate, and a lead plug inserted into the middle of the bearing.
Vertical load transfer process: crossbeam → top pre-buried steel plate → top connecting steel plate → top sealing steel plate → lead core structure laminated rubber bearing → bottom sealing steel plate → bottom connecting steel plate → bridge pier.
Horizontal load transfer process: pier → bottom footing bolt → bottom connecting steel plate → top sealing steel plate and shear tenon → top connecting steel plate → top pre-buried steel plate → anchorage member.
Shear modulus: 0.8 MPa, 1.0 MPa, 1.2 MPa.
Working temperature range: -25 °C to +60 °C.
Lead core quantity: single or multiple.
Shape: rectangular and round.
Always a pre-production sample before production;2 Years quality warranty.
Online Installation guide;Free replacement of damaged products within the warranty period.














